Numerical simulation is a computer research method that runs calculations based on a specific mathematical model to simulate actual physical processes.
It is the most powerful analysis tool for complex physical problems and engineering problems. Advanced numerical simulation technology integrates many disciplines such as mechanics, materials, computers, and physics.
It’s an important means for achieving innovative design and research and development of equipment. Two common applications in it are finite element analysis and computational fluid dynamics.
Numerical simulation is a computer research method that runs calculations based on a specific mathematical model to simulate actual physical processes. It’s a significant way to achieve innovative design and product development.
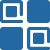
By integrating disciplines such as mechanics, materials, computers, and physics, numerical simulation suits perfectly for complex physical and engineering problems. The two most commonly used methods in a numerical simulation are Finite Element Analysis (FEA) and Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD).
FEA simulates real-world physical systems (geometry and load conditions) based on mathematical approximation. CFD uses numerical analysis to solve the equations of fluid mechanics in a computer to predict the flow of a flow field.
With Scantech world-leading 3D laser scanners, data of physical objects are precisely captured for FEA and CFD. Due to these accurate 3D point cloud data, engineers can simulate real physical systems, so as to help manufacturers solve complex manufacturing problems.